Featured thinking :
The art and science of hospital planning & design
Case studies, current trends, challenges, and critical factors
By : Urvish Patel
Designing a hospital isn’t just about putting up walls and filling them with medical equipment—it’s about crafting a space that seamlessly blends innovation, efficiency, and patient well-being.
In India, where the healthcare sector is rapidly evolving, hospital planning is both an art and a science. It’s about more than blueprints and budgets; it’s about creating a healing environment that meets the needs of patients, doctors, and the ever-changing medical landscape.
This article dives deep into the key elements that make hospital planning successful—from smart design principles to financial viability, compliance with evolving regulations, and real-life case studies. Whether you’re a healthcare investor, an architect, or a medical professional dreaming of building your own hospital, this is your guide to doing it right!
The Need for Strategic Hospital Planning
India’s healthcare landscape is rapidly evolving with increasing demand for quality medical facilities. Key factors influencing hospital planning include:
Population growth and demographic shifts
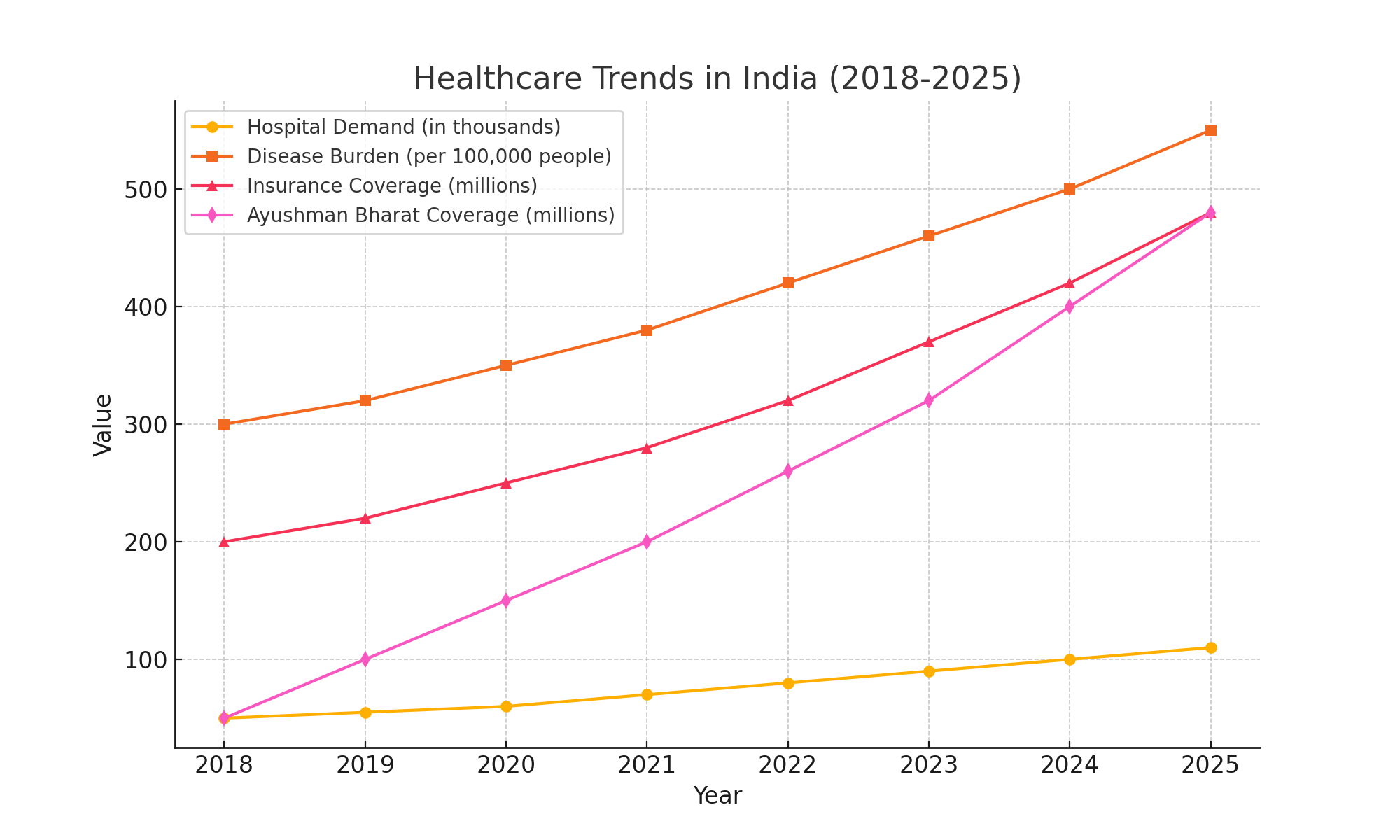
With populations booming and demographics shifting, the way we think about hospitals needs a serious upgrade. The old-school hospital model just won’t cut it anymore. Take aging populations, for example—by 2050, nearly 20% of India’s population will be over 60. That’s a massive shift that demands hospitals to be more senior-friendly, with features like fall-proof rooms, geriatric care wings, and rehabilitation centers tailored to elderly patients. At the same time, urban migration is packing cities with younger, tech-savvy professionals who expect AI-driven, high-efficiency hospitals where everything from check-ins to diagnostics is seamless and automated. Meanwhile, rural communities, which have long struggled with hospital access, need a network of decentralized mini-hospitals and telemedicine hubs to bridge the healthcare gap. The future of hospitals isn’t just about treating illness—it’s about predicting, preventing, and personalizing care to meet the unique needs of a rapidly evolving population.
Government regulations and accreditation standards (e.g., NABH, JCI, AERB, Fire Safety, Clinical Establishment Act)
When it comes to hospitals, regulations aren’t just red tape—they’re what keep patients safe and care top-notch. Standards like NABH and JCI set the bar for quality, while AERB ensures safe use of radiation in treatments. Fire safety laws prevent disasters, and the Clinical Establishment Act keeps shady hospitals in check. These rules make hospitals safer, more efficient, and worthy of trust—because in healthcare, there’s no room for shortcuts.
The Science of Hospital Design
The best hospital designs don’t just look good—they function seamlessly, ensuring that doctors can work efficiently, patients feel comfortable, and operations run smoothly. Smart hospital planning is a blend of precision, foresight, and adaptability. Let’s explore what goes into making a hospital not just operational, but exceptional.
Site Selection & Master Planning
Finding the right location for a hospital is like setting the foundation for a successful business. The site needs to be easily accessible—because in emergencies, every second counts. A hospital built too far from major roads or public transportation can mean delayed medical care for those who need it most. Future expansion is another crucial factor; hospitals must have the space to grow and adapt to evolving medical demands. Environmental impact is also key—sustainability should be a priority, ensuring that construction doesn’t disrupt ecosystems or contribute to pollution. And, of course, compliance with zoning laws and regulations can’t be ignored, as they ensure smooth operations without legal hassles down the line.
Functional Layout & Space Optimization
A hospital’s layout isn’t just about where to place rooms—it’s about making sure that medical teams can move swiftly and efficiently, reducing bottlenecks and improving patient care. High-traffic areas like emergency rooms, ICUs, and surgical suites need to be in prime locations to allow quick accessibility. Standardized room sizes help maintain consistency in operations, and smart space management ensures that every square foot is utilized efficiently. Infection control measures, such as negative-pressure rooms and high-quality air filtration systems, should be integrated from day one to prevent cross-contamination. A well-designed hospital doesn’t just make work easier—it saves lives.
Engineering & Technology Integration
Behind every well-functioning hospital is a powerhouse of engineering and technology. HVAC systems maintain optimal air quality and temperature, reducing infection risks. Medical gas pipelines must be precisely engineered to handle emergencies, while robust electrical backup systems ensure there are no interruptions during critical procedures. Hospitals today also rely on cutting-edge technology—AI-driven patient monitoring, automated diagnostic tools, and smart record-keeping are no longer futuristic concepts, but necessities. Safety measures, from fire suppression systems to disaster preparedness protocols, must be built into the hospital’s core infrastructure to ensure security for both patients and staff.
Compliance & Regulatory Standards
Rules and regulations may seem like hurdles, but they’re actually safeguards to ensure hospitals meet the highest standards of care. NABH and JCI accreditation ensure that quality benchmarks are met, while fire safety codes mandate robust suppression systems and clear emergency exits. Proper biomedical waste management isn’t optional—it’s essential to prevent environmental and health hazards. Regulations like the Clinical Establishment Act and AERB define crucial safety and operational benchmarks, helping hospitals maintain high standards. Though meeting these regulations adds to initial costs, non-compliance can lead to hefty penalties, loss of accreditation, and ultimately, a hit to revenue and reputation.
Smart hospital design isn’t just about aesthetics—it’s about functionality, safety, and future readiness. With meticulous planning and attention to detail, hospitals can create an environment that truly serves the needs of patients, medical staff, and the broader healthcare system.
The Art of Hospital Design
When you think of a hospital, do you picture a cold, sterile environment with harsh fluorescent lights and overwhelming noise? It doesn’t have to be that way! The best hospitals are not just treatment centers but places of healing, comfort, and efficiency. Great hospital design blends science with human-centered aesthetics, shaping experiences that reduce stress, promote well-being, and improve operational effectiveness. When a hospital is designed thoughtfully, it doesn’t just function well—it feels right.
Patient-Centric Design
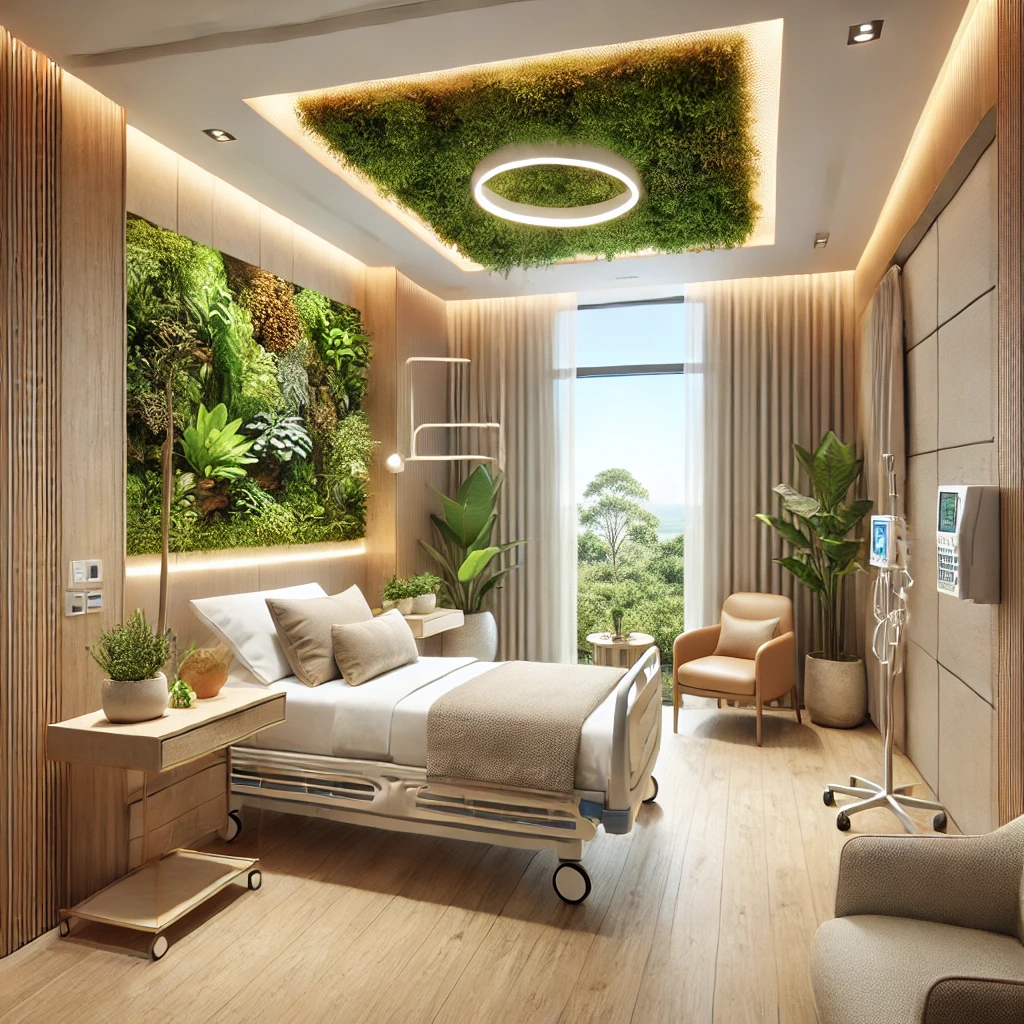

A hospital should be more than a building—it should be a sanctuary of healing. Research shows that architecture and environment directly impact patient recovery, and that’s why modern hospitals prioritize natural light, fresh air, and open spaces. Studies indicate that exposure to natural light speeds up recovery times, reduces depression, and improves sleep quality.
Biophilic design—bringing nature indoors—fosters a soothing atmosphere. Greenery, water elements, and earthy textures create a sense of tranquility, lowering stress levels for both patients and staff. Thoughtful acoustic design, soundproofing, and designated quiet zones help minimize the constant noise of alarms, machines, and bustling hallways, making rest and recovery easier.
Hospital furniture should be ergonomic, providing comfort for long-term patients and ensuring accessibility for those with mobility challenges. Wide corridors, wheelchair-friendly pathways, and intuitive signage aren’t just conveniences; they are necessities for a seamless healthcare experience. A well-designed hospital makes navigating the space effortless for everyone—patients, visitors, and healthcare workers alike.
Cultural and Regional Considerations
Hospitals should reflect the culture and values of the communities they serve. In India, incorporating spiritual spaces for prayer and meditation provides emotional support for families and patients. Culturally sensitive design—such as including areas for family gatherings, waiting spaces that respect privacy, and separate male and female prayer rooms—creates a comforting environment for diverse patient populations.
Using locally sourced materials doesn’t just add authenticity; it also reduces costs and improves sustainability. A hospital that respects its cultural and environmental context feels more welcoming and connected to its community.
Food plays a vital role in healing. Patients are more likely to eat well when provided with culturally familiar and nutritious meals. Hospitals should design food service areas that prioritize hygiene, efficiency, and dietary inclusivity—because food is medicine too.
Aesthetic & Interior Design
Nobody wants to feel like they’re trapped in a clinical, lifeless space. A hospital’s design should uplift spirits and create a calming atmosphere. Soft, muted colors like blues and greens have been scientifically proven to reduce anxiety. Instead of drab, uninspiring walls, why not bring in art? Murals, nature-inspired imagery, and interactive art installations have been shown to ease stress and even improve patient recovery times.
Hospitals should also implement intuitive wayfinding systems—color-coded floors, digital maps, and clear signage—so that visitors don’t feel lost in a maze of corridors. The goal? Make the hospital feel welcoming, not overwhelming.
Strategies for Smooth Execution of Hospital Planning
A well-planned hospital isn’t built overnight—it’s the result of meticulous strategy and collaboration. The key to avoiding chaos? Engaging multidisciplinary teams early in the process. Architects, engineers, doctors, nurses, and administrators must work together from day one to create a functional and efficient space.
Phased construction planning ensures that hospitals can remain operational during expansions or renovations, avoiding unnecessary downtime. Prefabricated modular construction—where hospital components are built off-site and assembled on location—can cut costs and speed up project timelines.
Most importantly, hospitals should think ahead. Gathering feedback from doctors, nurses, and even patients can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the facility meets real-world needs. Planning for future medical advancements, such as AI diagnostics and robotic-assisted surgery, ensures that hospitals remain cutting-edge for years to come.
Cost-Saving Alternatives Without Compromising Quality
Building a hospital is expensive, but there are smart ways to cut costs without sacrificing quality. Instead of opting for the cheapest materials, hospitals can invest in energy-efficient solutions that save money in the long run. Solar panels, LED lighting, and smart HVAC systems reduce utility costs while also being environmentally friendly.
Locally sourced, sustainable materials can lower construction costs while also making hospitals more eco-conscious. Designing flexible, multi-purpose spaces allows hospitals to adapt without expensive renovations. For example, a conference room can double as a telemedicine center, and outpatient clinics can be quickly transformed into emergency care units when needed.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency Through Smart Design
An efficient hospital isn’t just about great medical care—it’s about seamless operations. A well-planned hospital reduces bottlenecks, improves workflow, and ensures that doctors and nurses can focus on what truly matters: patient care.
Automation is revolutionizing hospital operations. Smart inventory management systems prevent shortages and reduce waste. Automated pharmacy dispensers improve medication accuracy and cut waiting times. Digital patient records streamline check-ins, consultations, and billing, reducing administrative headaches.
Centralized nurse stations with visibility over patient wards improve response times, reducing medical errors and ensuring that help is available when needed. RFID-based tracking for medical equipment eliminates wasted time spent searching for crucial devices. The smoother a hospital runs, the better the experience for both staff and patients.
Let’s build hospitals that don’t just meet expectations, but exceed them.
By incorporating these strategies, hospitals can become more than just treatment centers—they can become spaces of healing, innovation, and efficiency. A well-designed hospital doesn’t just function—it inspires confidence, reduces stress, and improves patient outcomes.
